Protein activity modulation with RU486.
Starting from the mutant rat glucocorticoid receptor by Prof. Sandro Rusconi (University of Fribourg, Switzerland), PolyGene has elaborated an enhanced RuX system with versatile and powerful properties for sensitive gene regulation in tissue culture and in vivo.
As opposed to sex hormone receptors, the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is mainly localized to the cytoplasm in hormone-free cells. Ligand binding triggers the translocation of GR through the nuclear
pore complex and, when bound to specific target sites within the chromatin, hormone-GR complexes influence the transcriptional activity of linked promoters (Pratt et al, 1993, DeFranco, 2002).
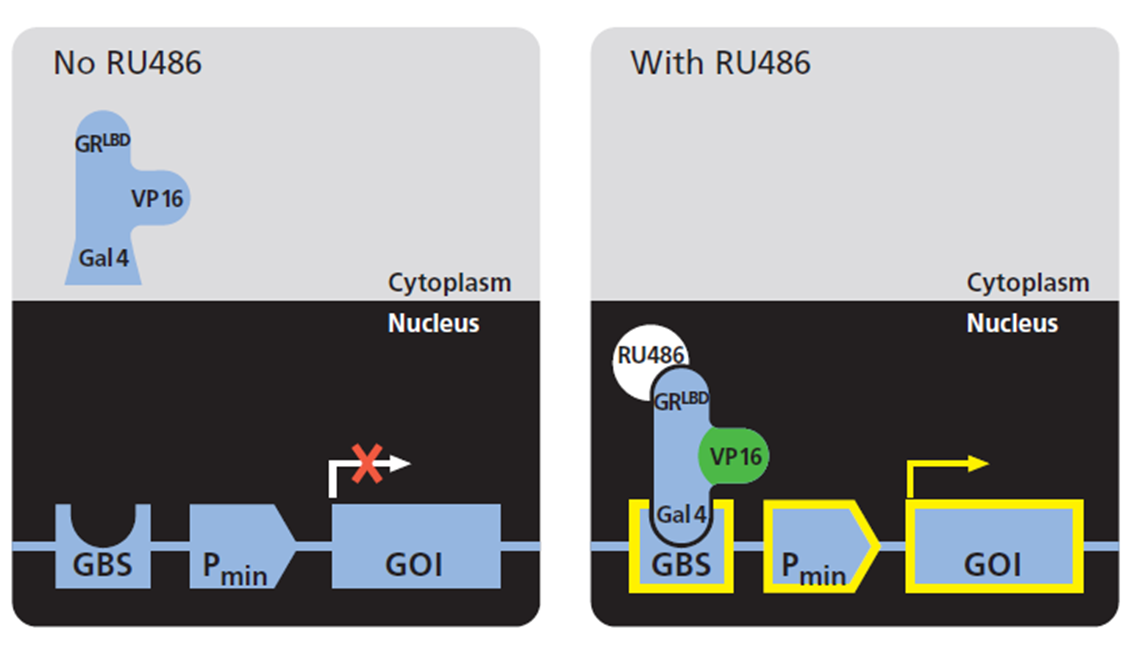
Breeding of complementary transgenic (EFFECTOR & RESPONDER) RuX mouse lines yields offspring, in which expression of a given Gene Of Interest (GOI) is induced with RU486.
Key features of this approach to regulating protein activity are unique in combination. On fusion of heterologous domains to GRLBD, it can function as a regulatory cassette and subject various protein functions to hormonal control (Picard et al, 1991).
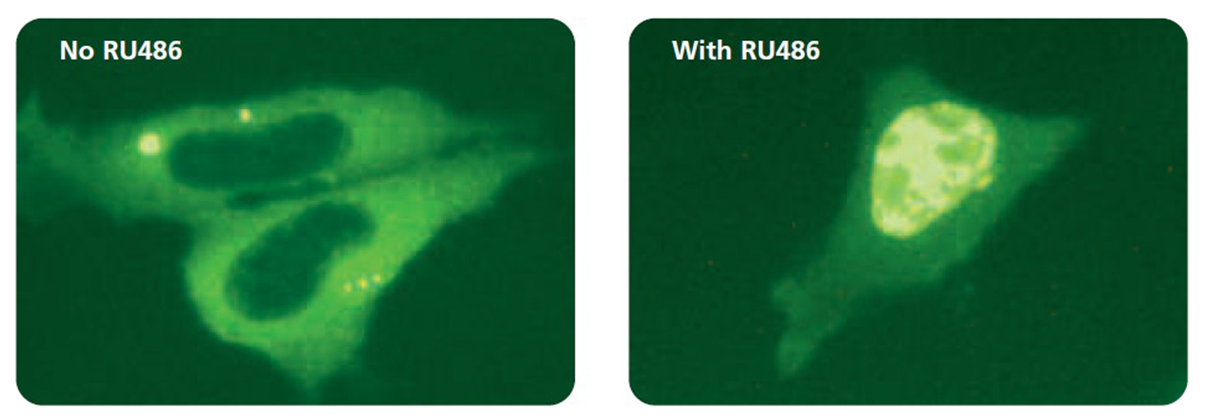
Left: Hormone-free culture, Right: With RU486
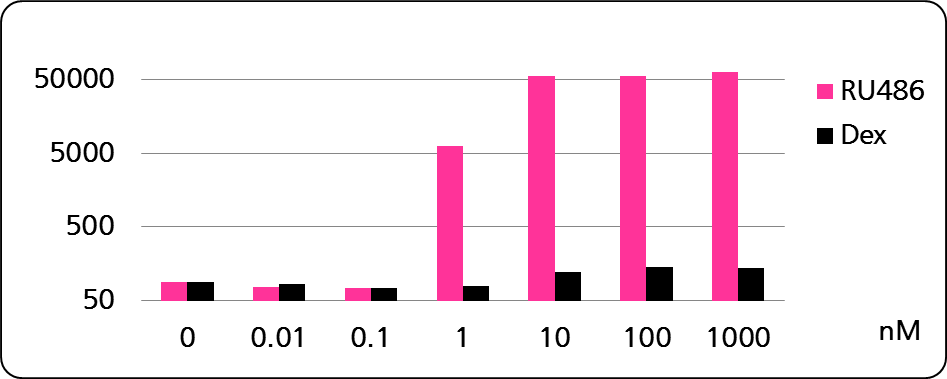
The strict nuclear translocation upon hormone binding of the glucocorticoid receptor also offers a unique way to configure cytoplasm-nucleus shuttling systems (e.g. the shuttling and activation of site-specific recombinases, or of marker peptides).
A conserved carboxy-terminal subdomain is Important for ligand interpretation and trans-activation by nuclear receptors.
Endocrinology 135 Nr 5, 2183-2195 (1994).
Pratt, W. B. and Scherrer, L. C.,
Steroid hormone receptors. In Moudgil UK (ed.), Heat shock proteins and the cytoplasmic-nuclear trafficking of steroid receptors.
Birkhäuser, Boston, pp. 215-246 (1993).
DeFranco, D. B.,
Navigating steroid hormone receptors through the nuclear compartment.
Mol. Endocrinol.16(7), 1449-1455 (2002).
Picard, D.,
Posttranslational regulation of proteins by fusions to steroid binding domains.
Methods Enzymol. 194, 373 (1991).
Wang, Y. et al.,
Ligand-inducible and liver-specific target gene expression in transgenic mice.
Nat. Biotechnol.15, 239-243 (1996).



