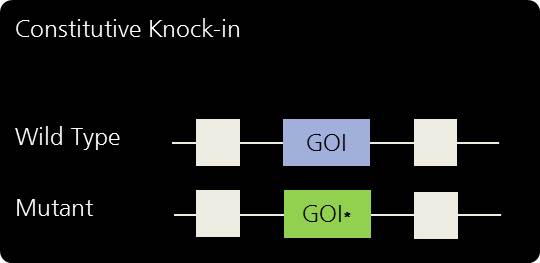
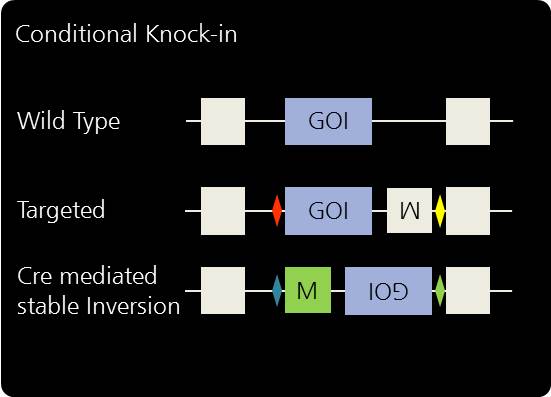
Gene replacement and humanization by knock-in.
Gene targeting by knock-in can mean to generate a point mutation corresponding to a human morbid gene; or to use the genomic regulation and insert a coding frame – a fluorescent marker, a recombinase, or another foreign gene – instead of the previously present gene.
Typically a knock-in is done in mice since the technology for this process is more refined and there is a high degree of shared sequence complexity between mice and humans.
We at PolyGene are specialized in difficult-to-achieve knock-in strategies in mice and rat. We offer constitutive and conditional knock-in strategies. Our clients have the full freedom to operate on knock-in animal models generated by PolyGene.Global and Permanent Gene Replacement by Constitutive Knock-in
Developmental, Temporal, or Tissue-specific Gene Deletion by Conditional Knock-in
Creation of Humanized Animal Models
Mice (or rats, rabbits) carrying certain human genes or loci (humanized mice, rats or rabbits) are increasingly important for pharmaceutical drug development and drug testing. This is because many mouse proteins differ in the overall protein structure from their human counterpart, meaning that e.g. drug binding affinities generated on the mouse protein cannot directly be used for studies in human.
PolyGene offers two different strategies for the generation of humanized mice, rats or rabbits:
The cDNA Approach.
We target the human gene (WT or mutant) into the endogenous mouse locus. It will be expressed under the transcriptional control of the endogenous mouse promoter, and therefore transcribed in exactly the same way as the native mouse gene.
We target the human gene (WT or mutant) into the endogenous mouse locus. It will be expressed under the transcriptional control of the endogenous mouse promoter, and therefore transcribed in exactly the same way as the native mouse gene.
The BAC Approach.
We inject a human BAC (piggyBAC) carrying your human gene of interest into mouse zygotes for the generation of transgenic humanized mice. Depending on the size of the BAC, the BAC may contain only the coding region of your human gene of interest, or also the human promoter region. Generally, the human expression system is equivalent to the mouse regulation, and we express equivalent expression profiles.
We inject a human BAC (piggyBAC) carrying your human gene of interest into mouse zygotes for the generation of transgenic humanized mice. Depending on the size of the BAC, the BAC may contain only the coding region of your human gene of interest, or also the human promoter region. Generally, the human expression system is equivalent to the mouse regulation, and we express equivalent expression profiles.
Case Study: Phenotype and Treatment Study in MMAuria Mouse Model
Methylmalonyl-Coenzyme A mutase apoenzyme (MCM, MMCoA) catalyzes the conversion of L-methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA using adenosylcobalamin.
In humans, deficiencies in this gene result in a severe metabolic disorder called methylmalonic acidemia, or methylmalonic aciduria (MMAuria). Both, complete ablations of the gene, as well as milder forms represented by variants with impaired function, are inherited as an autosomal recessive disease.
Methylmalonyl CoA (MMCoA) is a catabolite of propionyl CoA, and its accumulation leads to a life-threatening and chronic ketoacidosis.
The aim in this study was to generate novel mouse models of MMAuria that survive through adulthood but show clear biochemical and clinical signs of disease. PolyGene generated mice by knocking in a missense mutation to the murine Mut gene ( Mut-p.Met698Lys mutation) by embryonic stem cell targeting. To generate Mutko/ki mice, female Mutko/wt were crossed to Mutki/ki males.
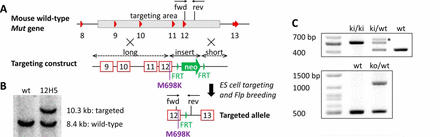
Generation of KI allele.
A, based on the wt mouse Mut gene, a targeting construct was generated to replace the Mut gene region spanning from introns 8 to 12, a missense mutation (p.Met698Lys) was inserted. Homologous recombination and Flp deletor breeding resulted in the final targeted KI allele with the mutation and one remaining FRT site.
B, Southern blotting of targeted clone 12H5.
C, upper panel, genotyping PCR of ear biopsy DNA for the KI allele. The asterisk indicates an additional heterodimer band as confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Lower panel, genotyping PCR of KO allele.
A, based on the wt mouse Mut gene, a targeting construct was generated to replace the Mut gene region spanning from introns 8 to 12, a missense mutation (p.Met698Lys) was inserted. Homologous recombination and Flp deletor breeding resulted in the final targeted KI allele with the mutation and one remaining FRT site.
B, Southern blotting of targeted clone 12H5.
C, upper panel, genotyping PCR of ear biopsy DNA for the KI allele. The asterisk indicates an additional heterodimer band as confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Lower panel, genotyping PCR of KO allele.
Adopted from publication: Novel Mouse Models of Methylmalonic Aciduria Recapitulate Phenotypic Traits with a Genetic Dosage Effect.